이 포스트는 Github 접속 제약이 있을 경우를 위한 것이며, 아래와 동일 내용을 관련 그림 및 실행 결과와 함께 Jupyter notebook으로도 보실 수 있습니다.
You can also see the following as Jupyter notebook along with related images and execution result screens if you have no trouble connecting to the Github.
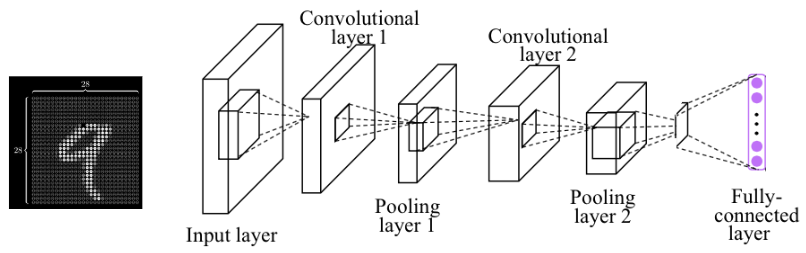
MNIST by CNN
import torch
import torchvision.datasets as dsets
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import random
USE_CUDA = torch.cuda.is_available()
device = torch.device("cuda" if USE_CUDA else "cpu")
print("다음 기기로 학습합니다:", device)
# 랜덤 시드 고정
random.seed(777)
torch.manual_seed(777)
# GPU 사용 가능일 경우 랜덤 시드 고정
if device == 'cuda':
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(777)
MNIST Data
mnist_train = dsets.MNIST(root='MNIST_data/',
train=True,
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
mnist_test = dsets.MNIST(root='MNIST_data/',
train=False,
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
Dataset 구성 확인
# MNIST dataset 크기
print("train data 크기:", len(mnist_train), " ", "test data 크기:",len(mnist_test))
# i번째 data 구성 요소확인
i=1234
print(type(mnist_train[i]), len(mnist_train[i]))
first, second= mnist_train[i]
print("first type :", type(first), " first len :", len(first), " first size :", first.size())
print("second type :", type(second), " second :", second)
- 2개의 tuple을 분리하여 first 성분을 확인해보니, 1 x 28 x 28 행렬(image)인 Tensor이고, second는 이 행렬의 Label 정보(정답)을 가지고 있다.
# image가 3차원이므로, 의미없는 1을 없애고 2차원으로 만들기 위해 view(28, 28) 진행하여 image확인
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(first.view(28, 28), cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
Data Loading
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
data_loader = DataLoader(dataset=mnist_train, batch_size=100, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
print(len(data_loader), type(data_loader))
- 전체 크기가 60000개인 data를 100개의 batch_size로 나누므로, data_loader는 600개 data로 구성됨.
- 이 때, data_loader의 한개 data는 자동으로 ‘100 x input차원’의 행렬이 된다.
Modeling
# 1. nn.Sequential 사용하여 Convolution Net 정의
# 이 때 ReLU 함수는 nn.ReLU()를 사용한다.
class CNN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
# 첫번째층
# ImgIn shape=(?, 28, 28, 1)
# Conv -> (?, 28, 28, 32)
# Pool -> (?, 14, 14, 32)
self.layer1 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
# 두번째층
# ImgIn shape=(?, 14, 14, 32)
# Conv ->(?, 14, 14, 64)
# Pool ->(?, 7, 7, 64)
self.layer2 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
# 전결합층 7x7x64 inputs -> 10 outputs
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(7*7*64, 10, bias=True)
# 전결합층 한정으로 가중치 초기화
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc.weight)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.layer1(x)
out = self.layer2(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1) # 전결합층을 위해서 Flatten
out = self.fc(out)
return out
mymodel = CNN().to(device)
# 2. Conv. ReLU, Rooling 직접 forward 연산 수행.
# 직접 forward 연산 시, ReLU 함수는 F.relu를 사용한다.
# nn.Sequential 사용에 비해, 계산 효율이 떨어짐.
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1,32, kernel_size=3)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32,64, kernel_size=3)
self.mp = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(1600, 10, bias=True) # Linear 함수의 input 차원을 직접계산하지 않더라도,
# Runtime Error 발생을 통해 그 값을 알 수 있다
# 전결합층 한정으로 가중치 초기화
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc.weight)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.mp(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.mp(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # FC 위해서 Flatten, x.size(0)는 batch size로 이는 고정, 나머지는 펼침.
x = self.fc(x)
return x
mymodel = MyModel().to(device)
# 3. MaxPooling과 ReLU 순서 변경했을 경우도 가능하나, cost 및 정확도가 조금 낮아졌음.
import torch.nn as nn
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1,32, kernel_size=3),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.ReLU())
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.ReLU())
self.fc = nn.Linear(1600, 10, bias=True)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc.weight)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
mymodel = MyModel().to(device)
학습
# optimizer 정의
learning_rate = 0.001
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(mymodel.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# Cost 정의
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device) # 소프트맥스 함수 포함됨.
training_epochs = 15
total_batch = len(data_loader)
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
for X, Y in data_loader:
# image is already size of (28x28), no reshape
# label is not one-hot encoded
X = X.to(device)
Y = Y.to(device)
hypothesis = mymodel(X)
cost = criterion(hypothesis, Y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
avg_cost += cost / total_batch
print('[Epoch: {:>4}] cost = {:>.9}'.format(epoch + 1, avg_cost))
print('Learning Finished!')
Test Data
# 서두에서 mnist_test가 10000개임을 확인했고, j번째 data확인
j=540
print(type(mnist_test[j]), len(mnist_test[j]))
test_first, test_second= mnist_test[j]
print("first type :", type(test_first), " first len :", len(test_first), " first size :", test_first.size())
print("second type :", type(test_second), " second :", test_second)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(test_first.view(28, 28), cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
Model 검증
- 위에서 mnist_test[j]의 image값인 test_first와 Label인 test_second로 model 검증
# 우선 위 mnist_test[j]를 검증
# conv2d의 input 차원은 4차원으로 '배치 크기 × 채널 × 높이× 너비' 로 구성되어야 함.
X_test1 = test_first.view(-1, 1, 28, 28).float().to(device) # model 함수 input 차원과 맞춤
Y_test1 = test_second
prediction = torch.argmax(mymodel(X_test1),1)
print(prediction)
print(prediction == Y_test1)
- 위에서 test_first 차원 지정없이 다음과 같이 정의하면 RuntimeError 발생하므로, 모르는 batch 차원은 -1로 지정
# minist_test 모든 data에 대해 정확도 통계 계산
# test_data, test_labels method로 전체 data 계산
with torch.no_grad(): # gradient 계산 않음.
X_test = mnist_test.test_data.view(-1, 1, 28, 28).float().to(device)
Y_test = mnist_test.test_labels.to(device)
prediction = mymodel(X_test)
correct_prediction = torch.argmax(prediction, 1) == Y_test
accuracy = correct_prediction.float().mean()
print('Accuracy:', accuracy.item())